You are here
Wed, 2013-02-27 18:58 — mdmcdonald
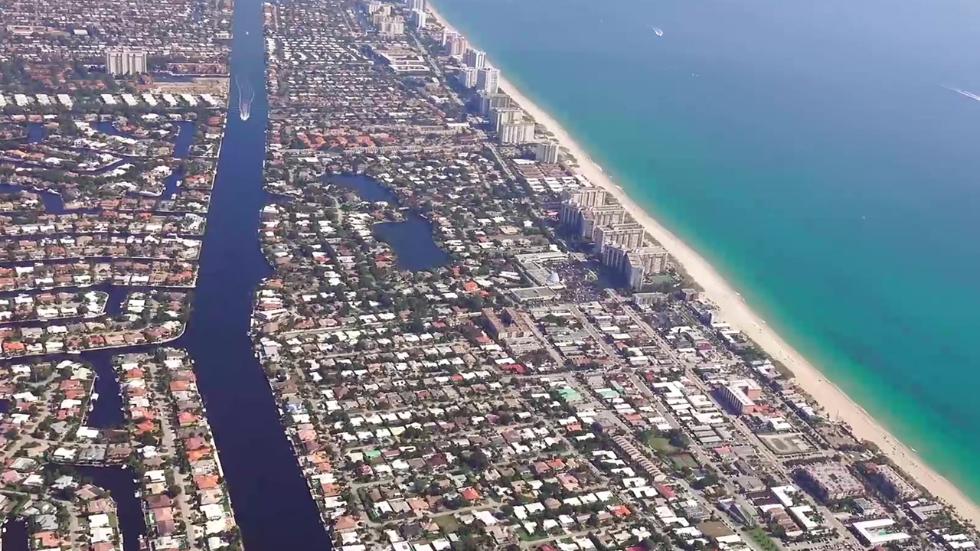
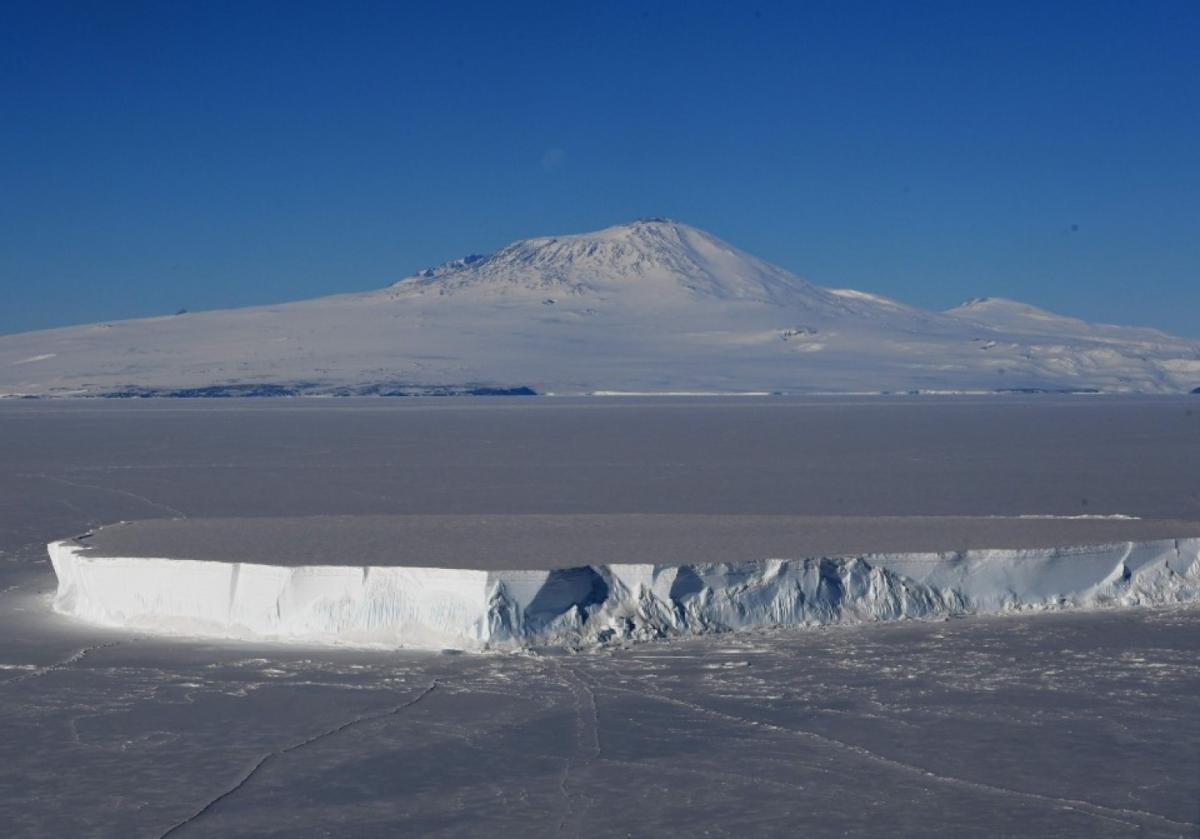
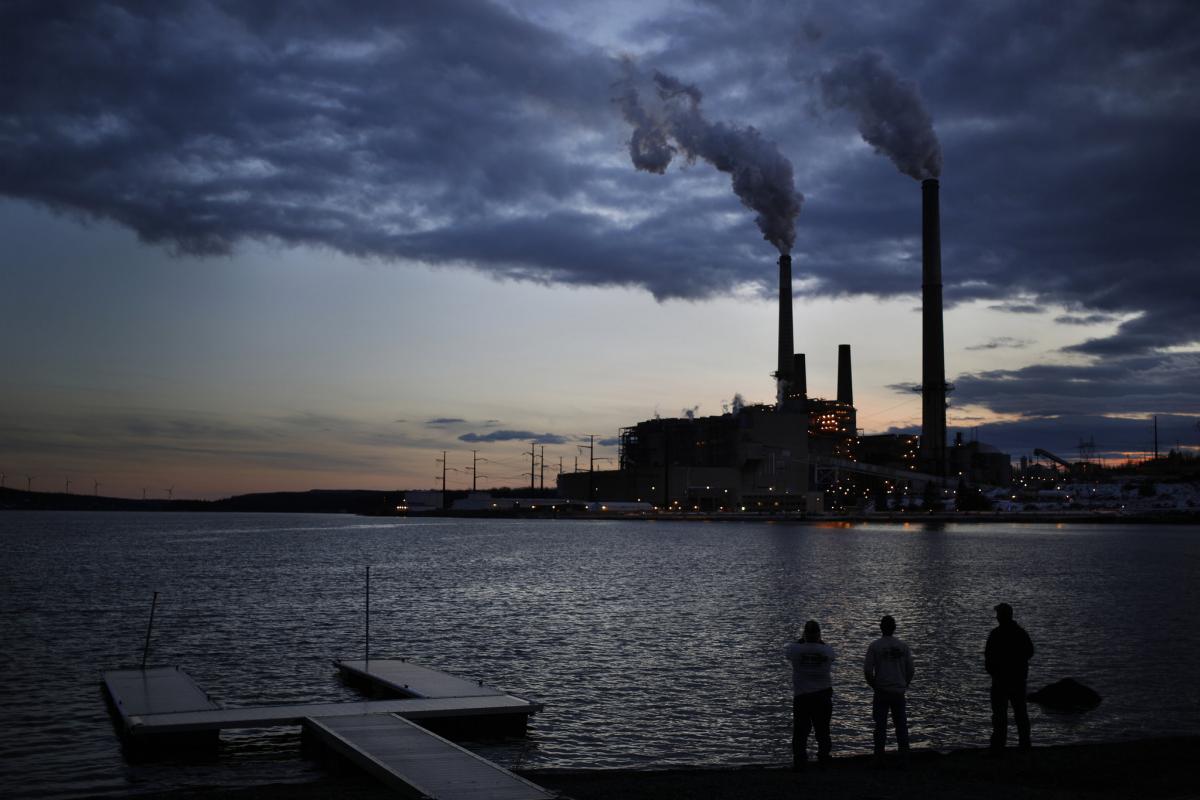
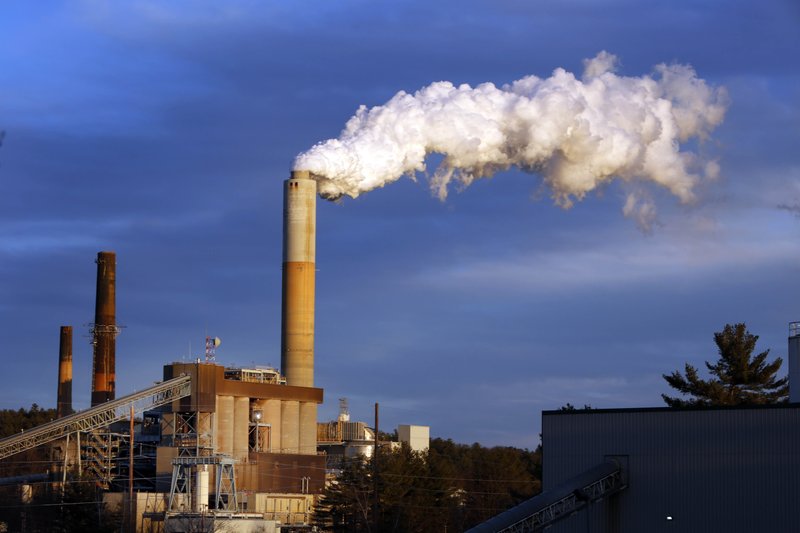
This working group focuses on the impact that climate change has on South Florida as well as factors that influence climate change.
To identify and manage factors that impact climate change as well as identifying and managing the impact that climate change is having on South Florida.
Add Content to this group
Members
| admin | Albert Gomez | ibague | Kathy Gilbeaux | mdmcdonald | MDMcDonald_me_com |
| Miles Marcotte | Shari Holbert |
Email address for group
climate-change-sfl@m.resiliencesystem.org
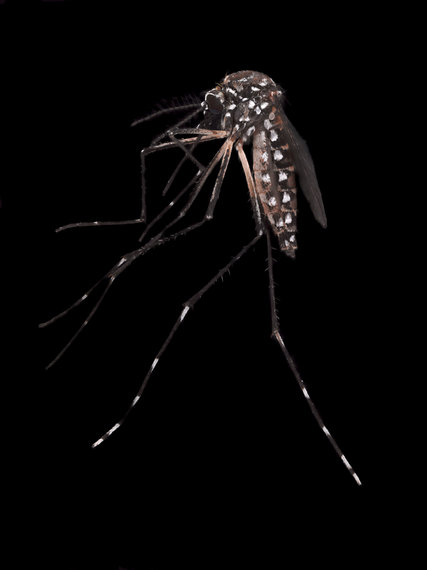









 Aedes aegypti. Credit Andrew Bettles for The New York Times
Aedes aegypti. Credit Andrew Bettles for The New York Times
Recent Comments